Molecular Composition of Retina in Aging & Disease
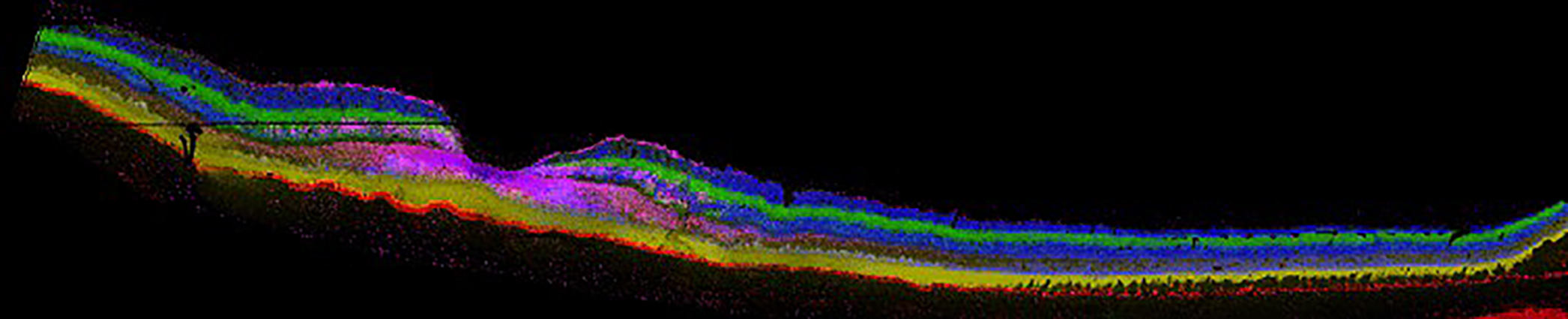
The retina is a complex and amazing tissue with an exquisite cellular architecture designed to transduce photons of light into electrical signals sent to the brain to provide our sense of sight. The cellular and molecular composition of the retina is still not completely characterized. Moreover, changes in cellular and molecular composition with age and in disease need to be elucidated to better treat retinal diseases.
The Schey lab has collaborated with researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina and the University of Alabama at Birmingham to define the molecular composition of retina layers and of retina deposits. Using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS), lipidomics, and fluorescence imaging, molecular features unique to each retina layer have been identified. In addition, molecular differences in macular and peripheral retina regions have been defined.
Our published imaging mass spectrometry results on the bisretinoid metabolite, A2E, led to the following quotation published in a letter to Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science:

Related References
Anderson DMG, Kotnala A, Migas LG, Patterson NH, Tideman L, Cao D, Adhikari B, Messinger JD, Ach T, Tortorella S, Van de Plas R, Curcio CA, Schey KL. Lysolipids are Prominent in Subretinal Drusenoid Deposits, a High-Risk Phenotype in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Front. Ophthalmol., 3:1258734, 2023.
Kotnala A, Anderson DMG, Patterson NH, Cantrell LS, Messinger JD, Curcio CA, Schey KL. Tissue fixation effects on human retinal lipid analysis by MALDI imaging and LC-MS/MS technologies. J Mass Spectrom., 56:e4798, 2021.
Grey AC and Schey KL. MALDI-MSI for Eye Diseases, in: MALDI MS Imaging: From Fundamentals to Spatial Omics, Porta T (Ed.), Royal Society of Chemistry, 2021.
Anderson DMG, Messinger JD, Patterson NH, Rivera ES, Kotnala A, Spraggins JM, Caprioli RM, Curcio CA, Schey KL. Lipid landscape of the human retina and supporting tissues revealed by high-resolution imaging mass spectrometry. J. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 31:2426-2436, 2020.
Anderson DMG, Ablonczy Z, Koutalos Y, Hanneken AM, Spraggins JM, Calcutt W, Crouch RK, Caprioli RM, Schey KL. Bis(monoacyglycero)phosphate Lipids in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Implicate Lysosomal/Endosomal Dysfunction in a Model of Stargardt Disease and Human Retinas. Sci. Reports 7:17352, 2017.
Bowery HE, Anderson DM, Pallitto P, Gutierrez DB, Fan J, Crouch RK, Schey KL, Ablonczy Z. Imaging mass spectrometry of the visual system: advancing the molecular understanding of retina degenerations. Proteom Clin Appl., 10:391-402, 2016.
Adler L, Boyer NP, Anderson DM, Spraggins JM, Schey KL, Hanneken A, Ablonczy Z, Crouch RK, Koutalos Y. Determination of N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E) Levels in Central and Peripheral Areas of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 14:1983-1990, 2015.
Anderson DMG, Ablonczy Z, Koutalos Y, Spraggins J, Crouch RK, Caprioli RM, Schey KL. High Resolution MALDI- Imaging Mass Spectrometry of Retinal Tissue Lipids. J. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25:1394-1403, 2014.
Ablonczy Z, Smith N, Anderson DM, Grey AC, Spraggins J, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, Crouch RK. The utilization of fluorescence to identify the components of lipofuscin by imaging mass spectrometry. Proteomics 14:936-944, 2014.
Ablonczy Z, Higbee D, Grey AC, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, Crouch RK. Similar molecules spatially correlate with lipofuscin and A2E in the mouse but not in the human RPE. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 539:196-202, 2013.
Ablonczy Z, Higbee D, Anderson DM, Dahrouj M, Grey AC, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, Gutierrez D, Hanneken A, Crouch RK. Lack of Correlation between the Spatial Distribution of A2E and Lipofuscin Fluorescence in the Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci, 54:5535-542, 2013.
Ablonczy Z, Gutierrez DB, Grey AC, Schey KL, Crouch RK. Molecule-specific imaging and quantitation of A2E in the RPE. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 723:75-71, 2012.
Grey AC, Crouch RK, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, and Ablonczy Z. Spatial Localization of A2E in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 52:3926-3933, 2011.
Gutierrez DB, Blakeley L, Goletz PW, Schey KL, Hanneken A, Koutalos Y, Crouch RK, Ablonczy Z. Mass Spectrometry Provides Accurate and Sensitive Quantitation of A2E. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 9:1513-1519, 2010.